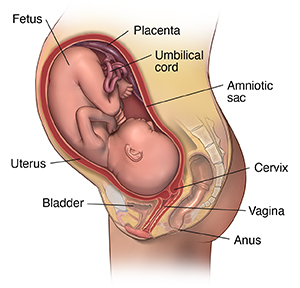
Anatomy: Fetus in Utero
Amniotic sac. A thin-walled sac that surrounds the fetus during pregnancy. The sac is filled with liquid made by the fetus (amniotic fluid) and the membrane that covers the fetal side of the placenta (amnion). This protects the fetus from injury. It also helps to regulate the temperature of the fetus.
Anus. The opening at the end of the anal canal.
Cervix. The lower part of the uterus that extends into the vagina. The cervix is made up of mostly fibrous tissue and muscle. It is circular in shape.
Fetus. An unborn baby from the 8th week after fertilization until birth.
Placenta. An organ shaped like a flat cake. It only grows during pregnancy. The fetus takes in oxygen, nutrients, and other substances from the placenta and gets rid of carbon dioxide and other wastes.
Umbilical cord. A rope-like cord connecting the fetus to the placenta. The umbilical cord contains 2 arteries and a vein. It carries oxygen and nutrients to the fetus and waste products away from the fetus.
Uterus. The uterus, or womb, is a hollow, pear-shaped organ in a woman's lower stomach between the bladder and the rectum. It sheds its lining each month during menstruation. A fertilized egg (ovum) becomes implanted in the uterus, and the fetus develops.
Vagina. The part of the female genitals behind the bladder and in front of the rectum that forms a canal. This extends from the uterus to the vulva.