What Is Bursitis?
A bursa is a fluid-filled sac. It helps cushion the muscles, tendons, and bones around a joint. When a bursa becomes inflamed, it’s called bursitis. Common symptoms are pain, tenderness, and swelling that limits movement of the joint.
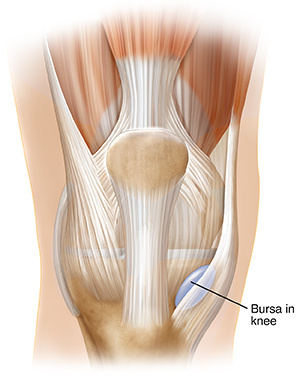
What causes bursitis?
Bursitis can be caused by a one-time event, such as a fall or blow to a joint. Bursitis is more commonly caused by overuse of a joint. The repeated movements bother the bursa and may cause it to swell. When that happens, other nearby tissues may become inflamed or have less space to move. Bursitis is most common in large joints, such as the knee, shoulder, elbow, and hip.
How is bursitis treated?
To help lessen pain and swelling, you may need one or more of these treatments:
-
Rest gives the bursa time to heal. This means limiting activities that put stress on the joint.
-
Ice may help. Put it on the area for 15 to 20 minutes several times a day. Wait at least 20 minutes between use, or as directed. Wrap the ice in a thin towel to prevent a skin injury.
-
Anti-inflammatory medicines help with painful swelling. In some cases, this can be shots of cortisone or other steroid medicines into the bursa.
-
Splints and supportive bandages improve your comfort. They also allow the bursa to heal.
-
Physical therapy may be used to gain flexibility and build up muscles that support the joint.
-
Aspiration removes extra fluid from the bursa using a needle. This can help your healthcare provider find out what is causing your bursitis. It might be an infection or overuse.
-
Surgery can be used to remove an inflamed or infected bursa. This is rarely needed.
Online Medical Reviewer:
Raymond Turley Jr PA-C
Online Medical Reviewer:
Stacey Wojcik MBA BSN RN
Online Medical Reviewer:
Thomas N Joseph MD
Date Last Reviewed:
8/1/2023
© 2000-2025 The StayWell Company, LLC. All rights reserved. This information is not intended as a substitute for professional medical care. Always follow your healthcare professional's instructions.